Three-dimensional (3D) rendering has a key role in industries that create realistic computer-generated images from models. It involves forming geometric shapes, textures, lighting and other realistic visual attributes that people can interact with on different platforms. It provides the ability to visually represent concepts, designs and related data in a more interactive, comprehensive, and informative manner than traditional ways. The current market size for visualization and 3D rendering software is expected to grow from $2.75 billion to $11.8 billion at a compound annual growth rate of 23.1% by 2029.
An immersive virtual reality (VR) 3D experience environment is primarily used by industries that are profoundly involved in designing and researching new components, such as equipment in defense, aeronautics, health information technology, architecture, education and heavy machinery.
Reasons for promoting the use of this technology include increasing demand for design review, customized products, real-time rendering and visualization, firsthand experience before launch, sales activities, etc. The following provides further explanation:
Manufacturing: Build digital twin prototypes, then review, refine and perform tests in a collaborative environment before actual manufacturing. These prototypes are used at marketing events to get user feedback and spark sales.
One of HCLTech's large engineering space clients has various configurations with their products. Building all prototypes is time-consuming and costly, so they decided to utilize 3D rendering techniques to visualize the products and get confirmation from their clients.
Healthcare: When training healthcare professionals, they must understand medical scans (CT, MRI, etc.), patient engagements and simulation surgeries, such as a knee replacement.
HCLTech is involved with Lifecycle and Healthcare (LSH) clients regarding surgical simulation use cases, e.g., joint replacement content, to train medical interns and doctors on understanding joint structure and related nerves to determine if 3D interaction helps retain knowledge.
Real Estate: Builders and buyers utilize 3D virtual tours to familiarize them with the property and visualize the interiors and exteriors of buildings. It helps them with sales and marketing activities.
An HCLTech client in real estate looked at the validation of insurance claim settlements. The exact 3D replica of buildings or flats and various equipment (fire equipment, HVAC systems, switchboards, etc.) within the buildings help builders and insurance companies settle claims submitted by clients.
Types of 3D environments
Apart from 3D rendering being used in games, animations, automotive, education, environmental science, etc., this experience is delivered in many ways, such as cave automatic virtual environment (CAVE) 3D Rooms, head-mounted display (HMD) devices and the metaverse.
CAVE: This is a completely immersive experience delivered through physical VR rooms. It is like a cave where the walls, ceiling and floor act as large projection screens surrounding the user, creating a sense of immersion in a virtual environment. CAVE is a localized experience, typically limited to a specific physical location.
HMD: These devices render 3D models near to your eyes, which is also known as near eye display (NED). HMDs (e.g., Oculus and HTC Vive) are typically more affordable and accessible to individual users. They offer a personal and immersive VR experience that can be used in various applications, including gaming, simulations and training. HMDs are portable and can be used in different locations, but they provide an individual experience rather than a shared one.
Metaverse: Multiple people interact with each other using their avatars in a virtual environment over the web using VR technologies. The metaverse concept is still evolving and there are different interpretations. It generally involves the convergence of VR, augmented reality (AR) and the Internet. The metaverse aims to create a seamless and immersive digital environment that goes beyond individual VR experiences. It is envisioned as a fully interactive and interconnected virtual world where users can explore, socialize, work, play and conduct various activities.
Although the purpose of utilizing these technologies differs, industries usually get confused about which is best suited for their requirements: CAVE, HMD or Metaverse? All three techniques utilize 3D rendered models, but there are significant differences in visualization experience and interactions.
Differences between CAVE- and metaverse-based VR environments
- Metaverse is a digital universe consisting of virtual shared space, AR/VR and Internet; while CAVE is an immersive VR system that consists of room-sized cubes with walls and projection systems.
- Metaverse is primarily conceptualized for an immersive and interconnected digital world where users can use digital avatars to socialize, play, shop, etc. In CAVE, physical users wear stereoscopic glasses and interact with a 3D virtual environment displayed on the wall. The CAVE system tracks the user’s movement and adjusts the visuals accordingly, resulting in a highly immersive experience.
- CAVE excels in niche applications, areas where precision and realism are crucial elements, such as scientific, astronomy, medical imaging and simulation, architectural walkthroughs, etc., while metaverse offers a broader and more versatile platform for a wide range of experiences and interactions. The choice between a CAVE and the metaverse depends on the specific goals and requirements of the project or application.
- The use of metaverse is mainly for communication, entertainment and eCommerce, while CAVE is used for scientific visualization, engineering simulations and research activities.
Differences between CAVE- and HMD-based VR environments
- CAVE provides a collaborative shared physical space where multiple users feel like they are part of the 3D world, while HMD isolates users from their surroundings and allows collaboration in the virtual world.
- Within CAVE, a user can move freely, but in HMD, movement is limited based on the initial boundary set.
- HMD is a single viewer per headset; CAVE is a multi-viewer experience in a physical space.
- CAVE is very costly, but HMD is budget-friendly.
Typical solution overviews of 3D rendering project
CAVE solution overview
In CAVE, a physical room is required to create a virtual environment where objects are projected via projections onto the walls and floors. Multiple projectors are used for seamless and immersive virtual environments. When a person enters into the physical room and interacts with the object through gestures, hand controllers or simply walks near the projected object. Multiple people can enter the room and interact.
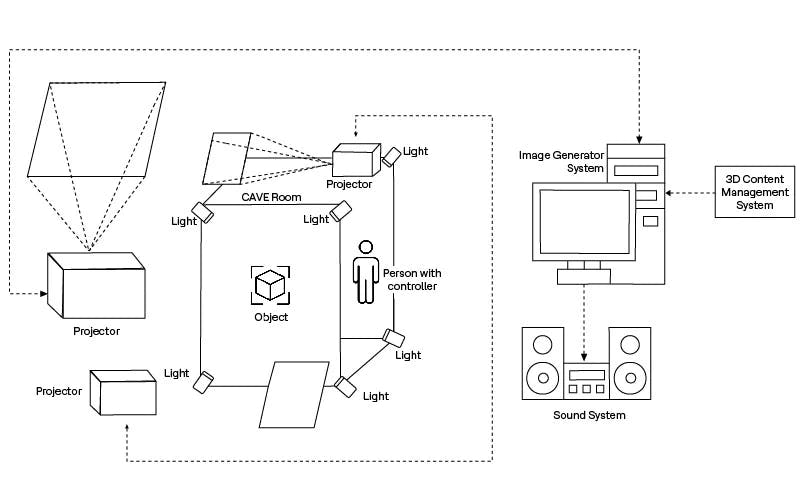
Figure 1: CAVE solution overview
Physical rooms are required in a CAVE experience. Based on room dynamics, chosen projection systems, lighting effects, sound systems, hardware and software are integrated.
Portability is not possible, like the HMD type of 3D rendering. However, the visualization and interaction with objects and rendering are seamless with a feeling of presence in the real environment.
Metaverse solution overview
The metaverse is a concept that requires virtual space created by the convergence of physical and virtual reality. The digital representation 'Avatars' are people involved in a virtual environment and interacting with interconnected virtual things with digital content. This is considered a digital virtual shared space with blockchain technology for ownership of virtual assets and decentralization
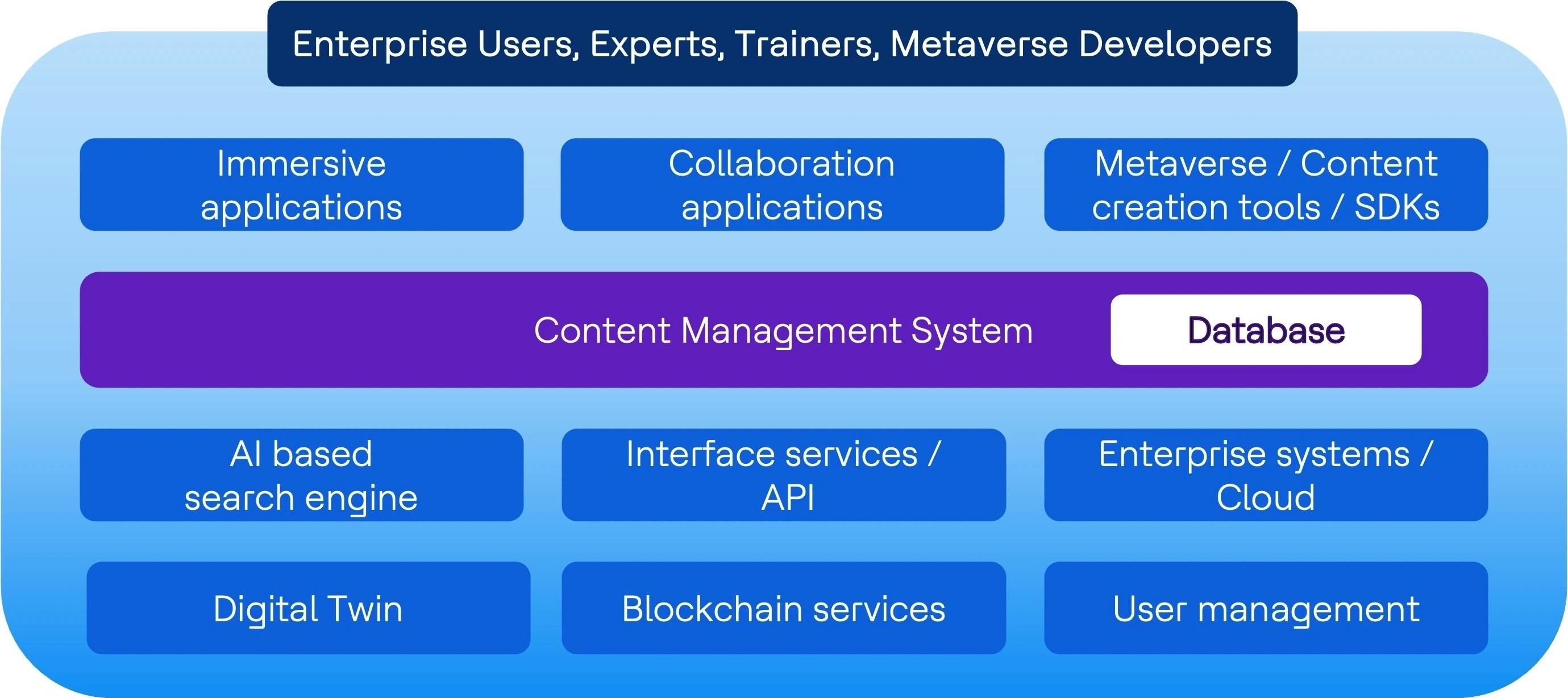
Figure 2: Metaverse solution overview
- Metaverse is a platform-based approach that requires data services, user management and interactions, digital twins, blockchain services and integration with enterprise systems.
- Robust networking is essential for seamless communication and interactions in the virtual space.
- Data governance and security is a must for sharing content in the virtual world.
HMD solution overview
Multiple users login to the virtual environment using a VR app hosted on a VR headset. They are able to visualize and interact with 3D models in a virtual environment to understand different aspects of representative equipment.
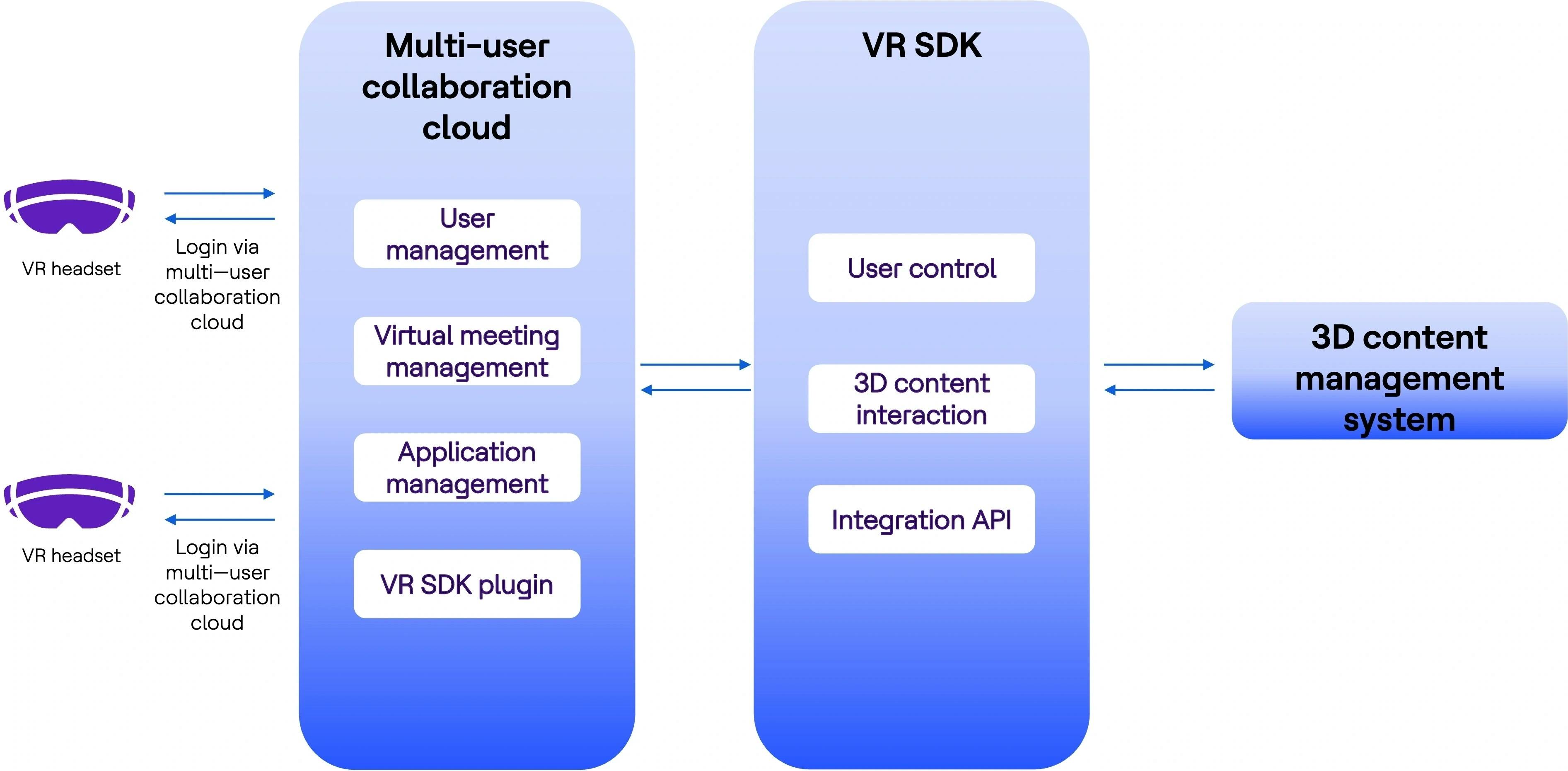
Figure 3: HMD solution overview
- Limited physical interactions with the real world can often produce motion sickness as it requires high frame rate and bandwidth due to hardware limitations.
- Users are isolated from real-world surroundings and potential to disorientation.
Key considerations for CAVE, Metaverse and HMD
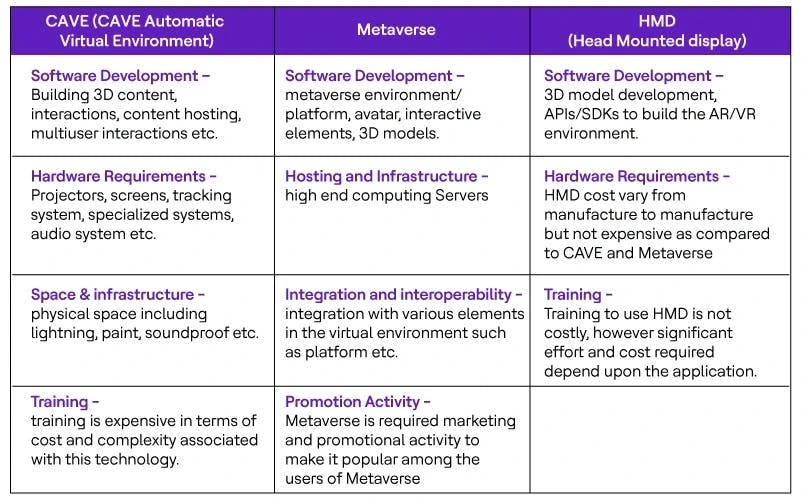
Table 1: Key considerations for CAVE, Metaverse and HMD solutions
HCLTech’s role in enabling 3D rendering
We have a significant role in 3D rendering projects, including:
- Consulting and assessment services: We help organizations understand specific needs and define goals to be achieved; assess existing processes, requirements and use cases to identify best fit technology in this space.
- Technology selection and recommendations: We provide recommendations on best hardware and software technologies to use in the setup based on expertise and exclusive partnerships in consulting and solutions.
- 3D model development and optimization: 3D models are the vital part of any 3D rendering project. This includes modeling, texturing, lighting, rendering and processing. Help is also offered to create 3D models to optimize existing models that can load and run faster in the environments.
- Software development and integration with various systems: Develop custom software applications tailored to specific needs includes creating software for 3D rendering, content creation, data visualization and interaction.
- Training and support: Provide operative training to get familiar with the software and hardware used in the system. Our support services ensure the smooth execution of the project over a longer duration.
- Project management: This is a very important activity to make a project successful. It includes management of vendors, resources, stakeholders, task scheduling activities, monitoring and communication.

