GenAI is an exciting field of AI that has the potential to mimic human creativity. Despite solid endorsements, however, organizations across industries are taking a cautious and measured approach toward embracing new GenAI tools in their business ecosystems. According to a recent survey conducted by VentureBeat, while more than half (54.6%) of organizations surveyed are experimenting with GenAI, only a small percentage (18.2%) are expected to spend more on technology in the year ahead. Many business leaders follow a 'wait and watch' policy before tapping into the new age of technology. While it's essential for organizations to carefully qualify the implications of adopting this technology, businesses must recognize such significant technological breakthroughs. The longer organizations wait to adopt GenAI, the further behind they may fall in terms of innovation and competitiveness.
Embarking on the GenAI journey may seem to be a daunting task initially. Still, a thoughtful approach can transform enterprise business operations, including productivity, efficiency, customer service and innovation improvements.
Ideate: Identify, evaluate and prioritize
GenAI is in its infancy. As a first step, businesses should call out the business pain points and work with experts to define business processes with customer touchpoints —these experts can help better assess which use cases are likely to bring the most value and can be implemented to validate the business value. A deeper assessment of the feasibility of addressing these use cases by using GenAI technology will help to create a strategic roadmap and identify a set of use cases that will lead to specific business values (like $ savings, $ revenue increment, customer experience improvement, efficiency, risk reduction, etc.) and are addressable based on problem complexity, technical feasibility and data availability.
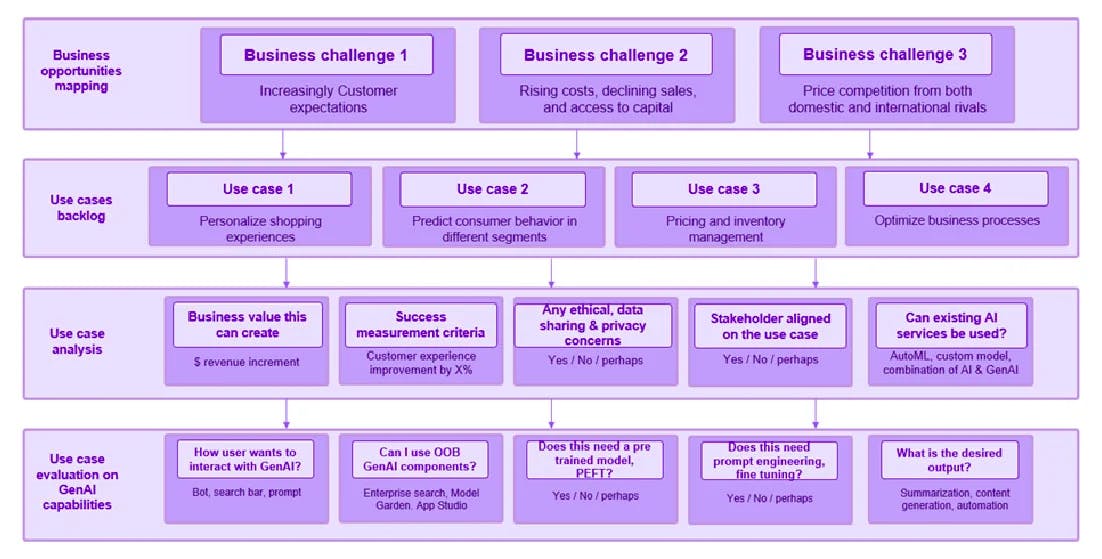
Figure1: Gen AI use case discovery framework
(Image crafted by the author to serve as a technical viewpoint)
Scoring criteria of use cases
Scoring (high, medium, low) each use case against the following criteria can help prioritize and identify those that are most likely to be successful in the business ecosystem. By carefully identifying and prioritizing the most promising use cases, organizations can maximize the benefits of GenAI, improve their bottom line and increase their chances of success.
- Alignment with strategic goals: How well does the use case align with the organization's strategic goals?
- Business impact: How much impact will the use case have? Can it be measured in terms of financial gains, efficiency improvement, etc.?
- Business processes: Will more than one business process/system be impacted? How many?
- GenAI product availability in GA: Are GenAI product assets available to be consumed in GA (general availability)?
- GenAI product maturity level: Is the GenAI product sufficiently mature to solve the use case fully?
- Prompt engineering: Are there any challenges with prompt design or prompt tuning? Impact on quality of response?>
- Customization requirements: Can out-of-the-box components and foundational models be used as is? Customization, PEFT (parameter efficient fine-tuning) requirements?
- Success criteria mapping: Are the measurable indicators that are relevant and significant to project success aligned well with business objectives?
- Risk assessment: What is the level of risk in the use case, including potential for technical issues or adverse public perception?
- Governance model: Stakeholders identified and aligned, roles and responsibilities mapped?
- Ethical considerations: Adherence to ethical guidelines, such as bias mitigation, responsible usage, etc.?
- Compliance alignment: Alignment with legal and industry-specific regulations?
- User experience and accessibility: How well does the use case meet the intended user experience? Is it accessible to all users?
- Monitoring and maintenance: Considerations for ongoing monitoring, maintenance and potential upscaling of the solution?
- Consumption: Consumption estimates for the use cases?
The landscape of GenAI offers a rich tapestry of opportunities that can be strategically explored across diverse business operations. Hence, it is advisable to prioritize use cases that balance high impact with minimal exertion.
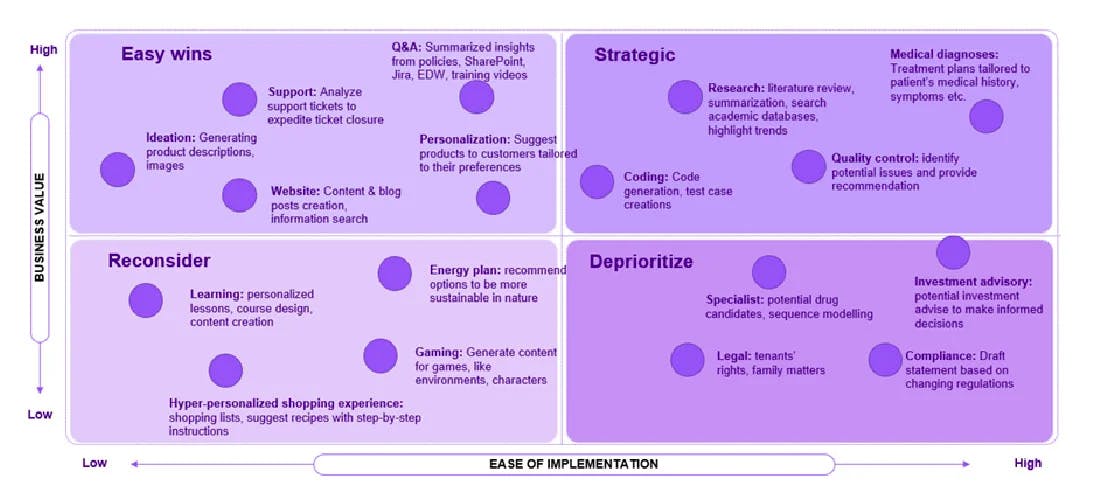
Figure2: Illustrative GenAI use case roadmap
(Image crafted by the author to serve as a technical viewpoint)
Infuse: Ethics, compliance, governance and risk management
When implementing GenAI within an enterprise environment, the stakes differ fundamentally from consumer applications. While consumers may engage with GenAI for entertainment or convenience, enterprises must integrate GenAI with a keen focus on enhancing operational efficiency and profitability. Integrating GenAI into business operations will help organizations free up resources, make better decisions and provide better customer experiences, leading to a competitive advantage and long-term success. However, this demands a robust consideration of ethics, compliance and risk in developing GenAI applications.
GenAI principles
Governance framework: A well-articulated and actionable governance for building, accessing and using GenAI is essential to mitigate potential risks and unintended consequences. Establish a comprehensive governance structure and enterprise-wide GenAI adoption framework. Implement a process that considers user interactions integration points across business functions and assess user access privileges to identify unauthorized usage; use enhanced cybersecurity protocols for data protection controls and data loss. Set up guidelines for human oversight to promote a balance between automation and human intervention.
- Compliance alignment: GenAI developments should adhere to regulations to avoid legal complications, violations, contract breaches, copyright infringement penalties and reputational damage. A thorough review of GenAI outputs in alignment with industry-specific and geo-localized laws, data privacy requirements or sector-specific guidelines and regulations is required. Identify applicable laws, regulations, policies, industry standards, etc.; assess the risk and identify data privacy violations and potential safety hazards; develop mitigation strategies by using fair and transparent algorithms; provide individuals control over their data; monitor and evaluate compliance on an ongoing basis with a human in the loop wherever possible.
- Ethical considerations: Building GenAI with ethical guidelines is imperative to prevent unintended and potentially harmful consequences. Address areas like bias, content integrity and responsible AI usage to ensure that the applications reflect the values and principles of the organization. Remain transparent with the data and algorithms used to train, advocate fairness by including data representing all domains and make people accountable by setting up clear policies and procedures for reporting and investigating incidents of bias or discrimination.
- Risk management: Different GenAI applications have varying levels of associated risks. While a chatbot error in a recipe might be minor, incorrect information in a compliance report or policy guidance can have serious repercussions. Understanding and evaluating potential risks and implementing appropriate safeguards and oversight mechanisms is crucial. Use established frameworks like NIST AI risk management framework to identify the risk, data privacy violations and potential safety hazards, work with data model owners to design control narratives and processes for manual intervention, engage the auditing team and others to de-risk generative AI use case developments.
- Continuous monitoring: An ongoing evaluation of GenAI applications is essential to identify evolving risks, compliance challenges and ethical dilemmas. Implement a robust GenAI monitoring framework to track model metrics for concept drift, toxicity and bias. Audit and test regularly to avoid inaccuracy; conduct impact assessments; establish monitoring models to identify drift, bias, standardization, transparency and feedback loops that align GenAI applications with the organizational goals and ethical standards.
By weaving these principles into their GenAI strategies, businesses can create a robust foundation that ensures responsible and effective utilization of generative technologies. The conjunction of innovation with ethics, compliance and risk management forms a sustainable path, helping organizations tap into the transformative potential of GenAI without sacrificing their core values and legal obligations.
GenAI app design considerations
- Contextual: Generate a natural, engaging, meaningful, relevant response to the target audience and avoid misunderstandings. Use domain-specific data, prompt engineering, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, etc.
- Accurate: Encourage transparency, present only verified results and strive for explainability in the generated content. Use task-specific LLM and present information sources like citations to help users validate the information
- Useful: Make efforts to mitigate bias, toxicity, randomness, hallucinations, harmful outputs, etc. Employ domain-specific data.
Integrate: Operationalize and scale
Businesses looking to embrace GenAI can embark on this journey in three progressive ways:
- Utilizing pre-built solutions: Initiating with ready-made GenAI applications like ChatGPT can offer a good entry point that requires almost no customization, allowing immediate experimentation and results.
- LLM integration using hyperscalers: Taking it a step further, businesses can use cloud services and employ APIs, such as Google's PaLM API, to fuse GenAI into their existing workflows. This offers greater alignment with specific enterprise needs without the complexity of building from scratch. From our recent Cloud Evolution survey report, of the 500 senior executives surveyed from 17 industries across 11 countries, 87% of those who have pivoted their business strategy in the past three years said they couldn't have done it without cloud.
- Bespoke GenAI customization: Develop customized GenAI models from scratch that align perfectly with unique organizational contexts for a tailored fit. This offers the highest degree of control but demands more resources and expertise.
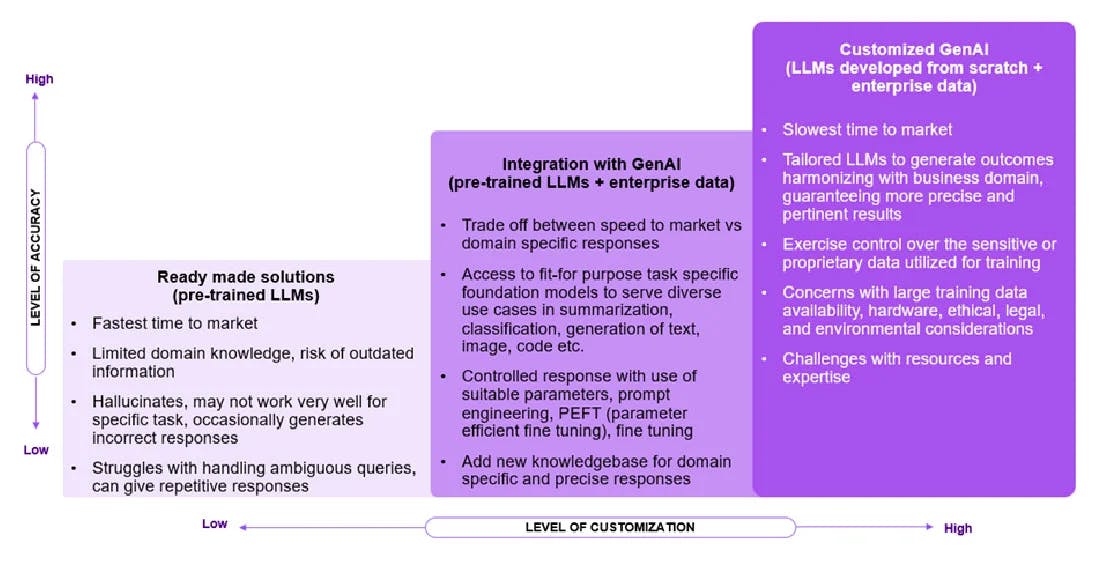
Figure3: Options to build LLM-powered applications
(Image crafted by the author to serve as a technical viewpoint)
By following this tiered approach, organizations can initiate a cautious foray into GenAI, monitor the progression and incrementally escalate their commitment based on the results. This methodical pathway ensures a balanced mix of innovation and risk management and can help organizations set the stage for transformative business enhancements.
Learn more: Google Cloud Ecosystem: Google Cloud and HCLTech Together | HCLTech





