Software-defined networking (SDN) is an innovative networking technology that empowers network administrators to efficiently oversee and govern network traffic through software, thereby eliminating traditional hardware-based monitoring methods. SDN not only facilitates the centralized management and security of networks by taking control over all devices, but it also orchestrates a fundamental architectural shift. This separation of network functions from hardware to software augments configurational and managerial flexibility, ultimately ushering in a new era for network administrators.
SDN separates the control of networking devices from the data processing functionality within the networking devices. This separation allows for more centralized management and flexibility when it comes to adapting the network to changing needs.
Components of SDN
SDN consists of following components:
- Management plane: This plane is responsible for the overall network management of the SDN environment. It includes the SDN controller, which acts as the central brain of the network and manages the entire system. The management plane handles tasks such as network configuration, monitoring, provisioning and policy enforcement.
- Control plane: This plane makes high-level decisions about how a network should operate. Acting as a bridge, it communicates with the management plane and translates the high-level network policies into low-level instructions for the data plane. The control plane uses protocols like OpenFlow to communicate with the data plane and manage network traffic.
- Data plane: The data plane or the forwarding plane is responsible for the actual forwarding of network traffic. It consists of switches or routers that are managed by the control plane. The data plane forwards packets based on the instructions received from the control plane.
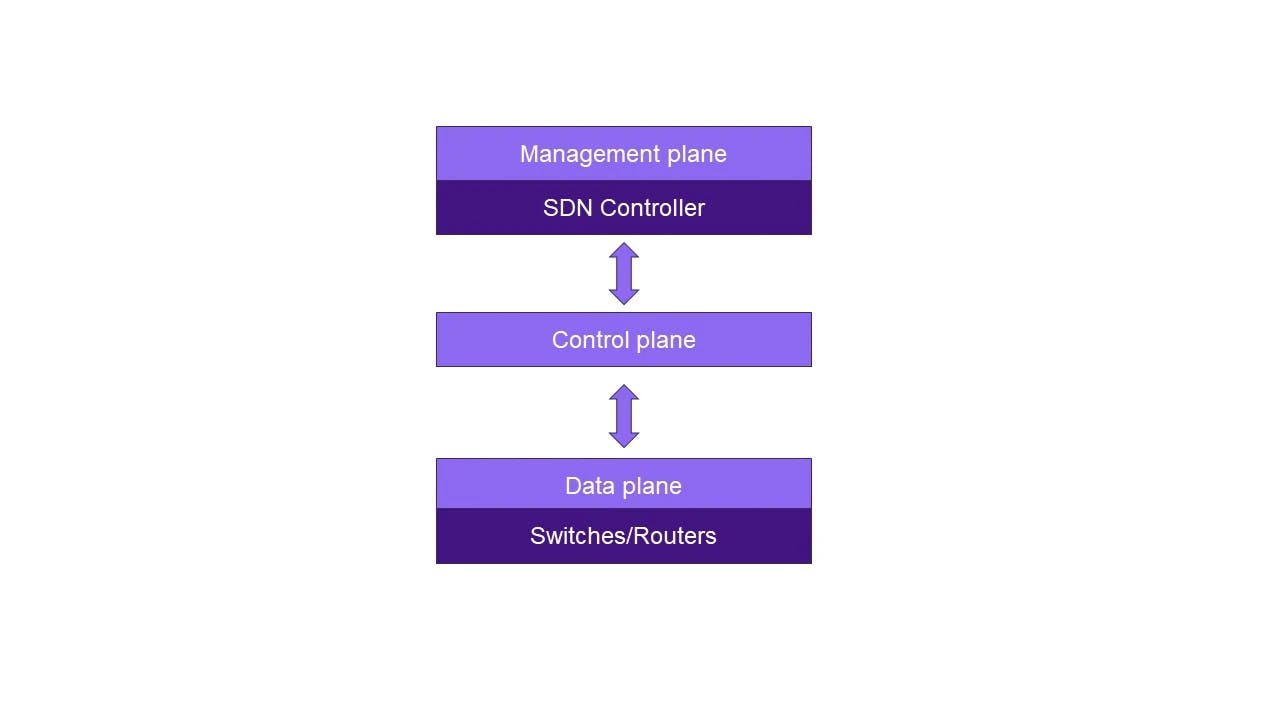
By separating the control plane from the data plane and centralizing control through an SDN controller, software-defined networking provides flexibility, agility and programmability to networks. It allows for efficient network management, dynamic and adaptive traffic routing and the ability to implement innovative network services and applications to streamline and simplify the responsibilities of network administrators.
Application of SDN in IoT
SDN is becoming increasingly important in IoT because it allows devices to communicate more easily and securely. SDN can also help reduce the cost of deploying and managing IoT networks.
SDN is essential for the development of IoT because it provides the flexibility and centralized management that is necessary for a network of objects that are constantly collecting and sharing data. SDN allows for the adaptation of the network to changing needs which is essential for a network that is constantly growing and evolving. SDN also allows for the centralized management of devices, which is necessary for a network that is spread out over a large area.
The advantages of using SDN in IoT Networks:
- Centralized control: SDN enables centralized control and management of the entire IoT network, allowing administrators to efficiently monitor, configure and update network devices from a single point of control. This provides better visibility and control over network management.
- Scalability: SDN helps in scaling IoT networks by allowing for the easy addition and removal of devices without complete manual configuration as the number of IoT devices increases.
- Enhanced security: Security is a critical concern in IoT networks. SDN allows for centralized security policies, making it easier to implement and enforce security measures across the entire network. It helps in threat detection for IoT devices.
- Traffic optimization: SDN helps in efficient traffic routing and load balancing in IoT networks. It ensures that data flows through the most optimal paths. This helps in improving network performance and reducing latency.
- Resource optimization: With SDN, administrators can optimize resource allocation in IoT networks. They can allocate bandwidth dynamically, prioritize critical traffic, and optimize network resources based on real-time requirements. This helps in improving overall network efficiency.
Potential drawbacks of using SDN in IoT networks:
- Single point of failure: Since SDN relies on a centralized SDN controller, any failure in the controller can have a major impact on the entire network. This single point of failure can potentially disrupt operations until the controller is rectified.
- Network dependency: SDN in IoT networks heavily relies on network connectivity and uninterrupted communication with the SDN controller. In case of network outages or connection issues, the network may become inaccessible or experience limited functionality.
- Latency: The dependency on a centralized SDN controller can introduce additional latency into the network. All decisions and routing instructions must pass through the controller, which can introduce delays in data transfer to network devices, especially in large-scale IoT deployments.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing software defined networking in IoT networks requires expert knowledge and specialization. It can be complex to set up and configure, requiring administrators to have a deep understanding of SDN concepts and protocols.
- Cost: Implementing SDN in IoT networks may require additional investments in hardware, software and expertise. The cost of acquiring and maintaining SDN infrastructure, specialized controllers and compatible devices may be higher compared to traditional networking solutions.
In conclusion, Software Defined Networking (SDN) stands as a transformative force in network administration. However, the decision of whether to implement SDN is dependent upon distinct requisites, scale considerations and available resources. A comprehensive assessment and evaluation of advantages and potential implications is imperative to guide the decision-making process.



