The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI (GenAI) into the healthcare industry introduces countless possibilities for improving patient care and outcomes. GenAI has the potential to revolutionize the way healthcare professionals gather and analyze data for diagnosis and treatment.
According to a December 2023 Gartner Healthcare Provider Research Panel survey, 84% of healthcare provider executives believe large language models (LLMs) — the foundation of GenAI — will have a significant (35%), transformative (37%) or disruptive (12%) impact on the healthcare industry overall.
However, several barriers exist on both the vendor and user sides that must be overcome for its successful implementation.
This article will delve deeper into the potential impact of GenAI on healthcare, exploring key challenges and detailing its short-term, mid-term and long-term applications.
Unlocking the power of data
One of the key challenges facing GenAI in healthcare is the availability of quality data. While healthcare generates vast amounts of data, much of it is not suitable for AI analysis. Historically, data collection in healthcare has been driven by current use cases, rather than for AI. As a result, efforts must be made to collect and curate data specifically tailored to support AI use cases. By gathering and refining accurate and representative data, healthcare professionals can maximize the potential of GenAI in delivering accurate diagnoses and treatments.
Overcoming development and security barriers
In addition to data challenges, the implementation of GenAI requires a significant development and effort barrier. To maximize the potential of AI, automated data collection from Internet of Things (IoT) devices is necessary, replacing the manual data input often still used. Real-time data collection facilitated by IoT devices can provide continuous and accurate patient information for AI analysis, enabling healthcare professionals to make better-informed decisions.
Furthermore, cybersecurity is a paramount concern in healthcare, as it is one of the most targeted industries for cyberattacks. To address this, cybersecurity vendors are now focusing on securing AI solutions by design, with healthcare-specific areas in data centers and compliance with data privacy regulations in mind. This ensures that patient data remains protected while GenAI technologies are utilized to improve healthcare outcomes.
Despite these challenges, the December 2023 survey revealed that most healthcare organizations (78%) are formally assessing use cases, while 66% are developing the ethics and policies for appropriate use and 47% are funding initiatives.
The role of cloud computing
“GenAI holds the key to unlocking a new era in healthcare, where data-driven insights pave the way not only driving improved health outcomes, but also enhance patient engagement and supercharge the administrative and operational value chain supporting patient care,” says Shrikanth Shetty, Chief Growth Officer, Life Sciences and Healthcare at HCLTech.
The utilization of GenAI in healthcare relies heavily on cloud computing. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions allow for the scalable deployment of AI models while ensuring data privacy regulations are abided by. Additionally, sovereign clouds may be employed to further enhance data protection and security. Leveraging the power of cloud, healthcare organizations can access AI technologies on demand and efficiently process and analyze large volumes of data, enabling more accurate and personalized patient care.
Short-term applications of GenAI
In the short term, the implementation of GenAI in healthcare has already shown promising results. Natural Language Processing (NLP), a field within AI that focuses on teaching machines to understand human language, is a leading area of development. ChatGPT, the AI engine excelling in NLP, can be integrated into healthcare settings, enabling functions such as ambient scribing to reduce the burden on clinical documentation. This technology facilitates real-time digital note-taking during patient consultations, alleviating the administrative burden on healthcare professionals.
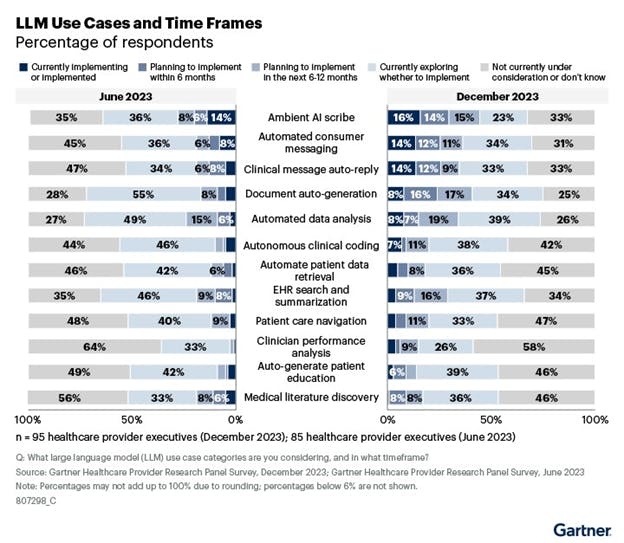
According to the December 2023 survey, 16% are currently implementing or have implemented an Ambient AI Scribe, while 14% are planning to implement it in the next six months and 15% in the next six to 12 months.
Furthermore, automated consumer messaging, clinical message auto-reply and document auto-generation are being explored as additional use cases. These functionalities streamline communication between healthcare providers and patients, ultimately improving patient experience and care.
Mid-term applications of GenAI
Looking ahead, the mid-term goals for GenAI in healthcare involve the incorporation of data science teams within hospitals. By empowering AI engines with the ability to understand natural language requests for data, healthcare professionals will no longer be reliant on IT departments to access and analyze data from multiple sources. This streamlining of the data analysis process will save time and allow for more efficient decision-making. AI-powered tools can help healthcare professionals extract relevant insights from medical records, research studies and patient-generated data, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans.
Long-term vision for GenAI
In the long term, the ultimate vision for GenAI is one in which AI becomes the doctor itself. Previous AI development has been primarily focused on pattern recognition, particularly useful in areas such as cybersecurity and early cancer detection. In some cases, the accuracy of certain cancer diagnoses has reached an impressive 98.35% with AI and machine learning.
However, GenAI expands its focus to include the language analysis of clinical diagnoses. By teaching AI engines, the language and patterns of diagnostic information, GenAI considers not only medical images but also factors like blood work and doctors' notes to make accurate diagnoses. This holistic approach to diagnosis offers healthcare professionals a comprehensive view of the patient's health and assists in formulating more individualized treatment plans.
Overcoming challenges and achieving widespread adoption
The widespread adoption of GenAI in healthcare faces challenges. The computing power required to support such technology is not yet fully understood, and the associated costs may skyrocket. This presents potential obstacles for vendors and end users alike.
However, government subsidies may play a role in offsetting these costs and encouraging the adoption of GenAI. Countries that invest in AI will likely witness significant social impact, leading to healthier and happier populations. It is important to foster collaboration between vendors, healthcare organizations and governments to address these challenges and drive the widespread adoption of GenAI.
The integration of GenAI into healthcare holds immense potential for transforming patient care. By leveraging advanced AI techniques and overcoming data and security challenges, healthcare professionals can harness the power of GenAI to provide more accurate diagnoses, streamline data analysis processes and ultimately improve the overall well-being of populations.
To fully realize these benefits, collaboration between vendors, healthcare organizations and governments is crucial in driving the widespread adoption of GenAI. With continuous advancements, GenAI has the capability to revolutionize healthcare and create a future where AI-based technologies work seamlessly alongside healthcare professionals, resulting in better health outcomes for all.





