Alan Turing, often touted as the father of theoretical computer science, remarked on a BBC program in 1951, “..it is not altogether unreasonable to describe digital computers as brains...I think it is probable for instance that at the end of the [20th] century it will be possible to program a machine to answer questions in such a way that it will be extremely difficult to guess whether the answers are being given by a man or by the machine.” Indeed, the man credited with cracking the German Enigma Code during World War II could not have been more accurate. With AI advancing at a breakneck pace, the computer ‘brain’ is constantly evolving!
Imagine that just about a year or so back, industry leaders were going gaga over this new kid on the block called Generative AI. LLMs were hogging discussions from tech war rooms to board rooms. That continues now as well, with even greater vigor. However, now we have agentic AI donning the limelight. In other words, the AI pie is getting not just more delicious, but larger too!
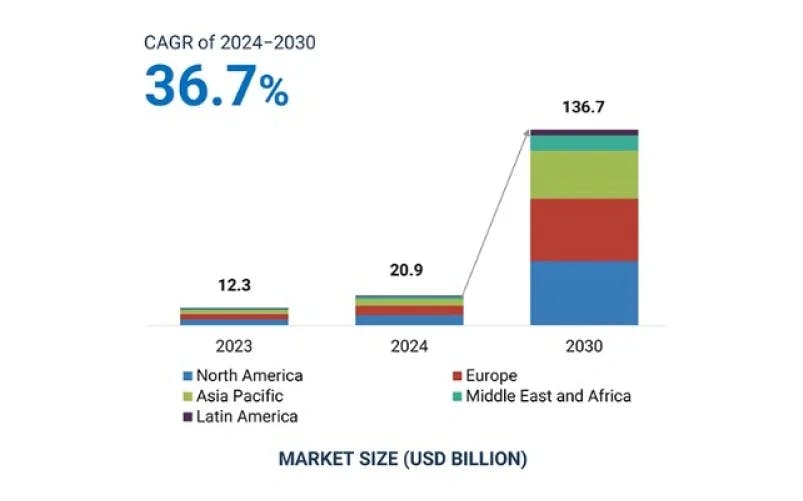
Growth trajectory of Agentic AI
Generative AI market size globally is expected to grow from USD 20.9 BN in 2024 to USD 136.7 BN by 2030. That’s a phenomenal CAGR of 36.7% during this period.
Compare that with the growth of Agentic AI market size, from USD 5.2 BN in 2024 to ~ USD 196.6 BN by 2034, translating to a CAGR of 43.8%. Out of possible Agentic AI applications, the ready-to-deploy segment occupied a lion’s share of 58.5% of the global market.
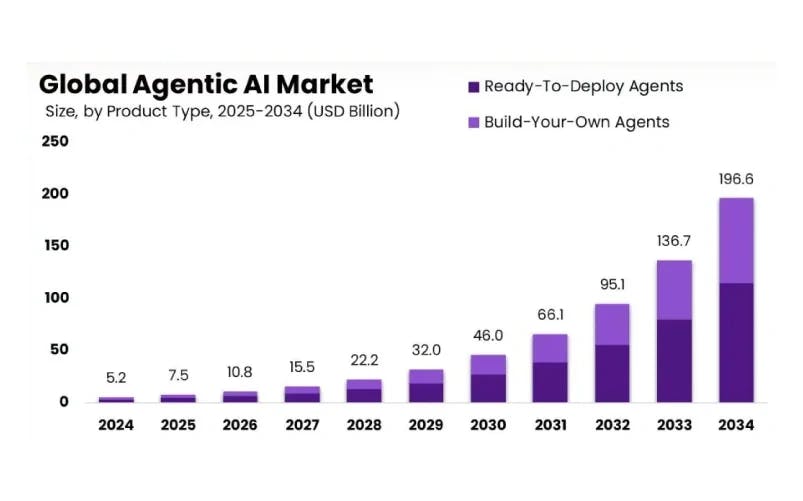
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position in the Agentic AI space, constituting more than 38% of the global market share, and generating ~ 1.97 BN in revenue.
But what exactly is Agentic AI? And how is it different from other forms of AI?
What is Agentic AI
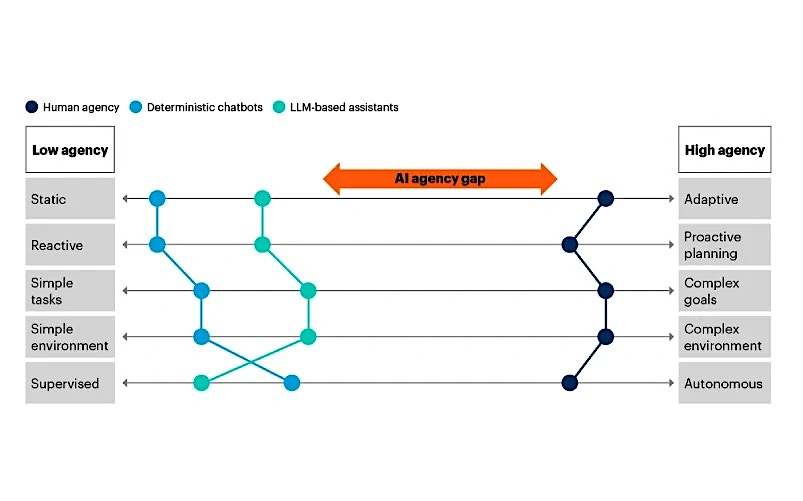
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that possess the capacity to make autonomous decisions and take actions to achieve specific goals with limited or no direct human intervention. These systems are more self-sufficient and embedded with reasoning capability that can not only respond to a human command, but chart out a set of successive actions as part of an autonomous or semi-autonomous workflow to achieve a desired end-goal.
Key benefits include:
- Enhanced decision-making: Agentic AI systems can analyze vast volumes of data and provide insights with an improvised set of actions. The insights can range from opportunities for revenue generation, cost take-outs, identify market trends, personalize recommendations and more.
- Improved efficiency: Agents can manage the set of routine tasks, while humans can be engaged in more productive activities. Errors can be reduced as well.
- Enhanced customer experience: By offering more personalized recommendations and outputs, agents can inherently enhance customer experience a lot more than other forms of AI. A high-agency environment can lead to handling more complex tasks, in a proactive and adaptive fashion.
A lucid example can be around employing AI agents for writing a blog. Let us detail this functionality with a workflow diagram.
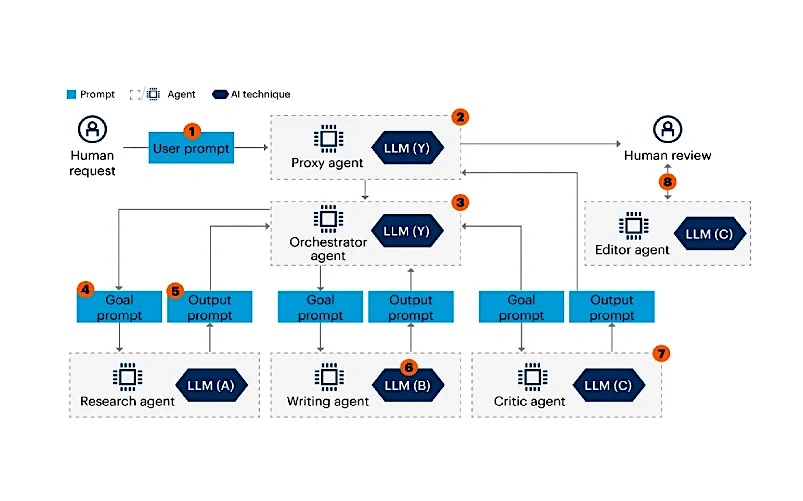
- User requests to write a blog
- Communicates with the human
- Coordinates capabilities of other agents
- Subgoal – Prompt to next agent
- Subagents return their output
- Agents in a MAS may use different LLMs
- Self-reflection or self-critique
- Human and AI agent coworker relation
How can AI agents help CPG firms
From what we just discussed above, it is evident that an autonomous or semi-autonomous decision-making engine as an AI agent can help CPG firms in a multitude of ways.
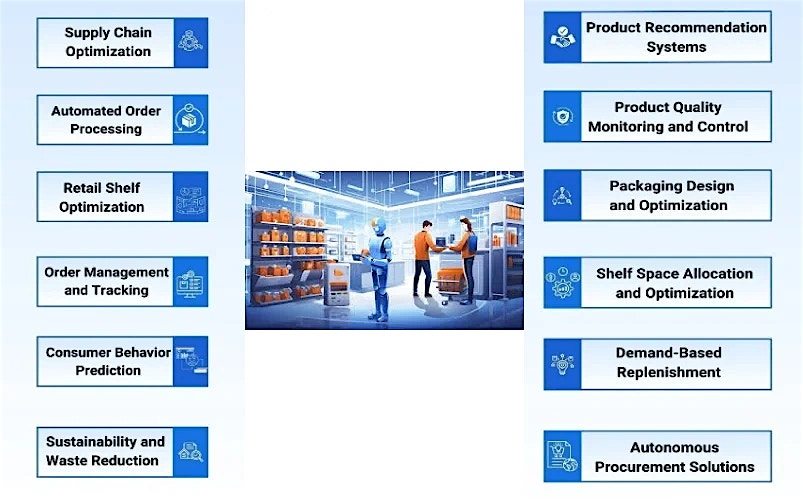
- Recommendation systems: Previous purchases and the consumer digital footprint can be analyzed to recommend SKUs and place the order using agents, that have been trained on vast volumes of customer data – across demographics, locations, etc.
- Warehouse management: The set of inbound and outbound processes, or portions of it, can be automated using agents. Processes such as receiving goods, maintaining accurate inventory control, generating trailer loading charts (which SKU maps to which trailer, considering optimization scenarios) and more can be automated to improve efficiency and speed order processing.
- Order management and tracking: From order placement to delivery, agents can process and track the orders, resulting in improved OTIF and better customer satisfaction.
- Supply chain optimization: Using a multi-agent system, disruptions within supply chain can be tracked effectively (and preemptively on occasions), and alternate parameters like routing can be prompted. This leads to a much greater efficiency for CPG supply chains.
- Product quality monitoring: AI agents can use ML and computer vision to preemptively detect errors across manufacturing lines, including any product or packaging defect, and prescribe a planned downtime for machines or segregate defective products for remedial actions. This reduces customer returns, leading to reduced reverse logistics cost and better customer experience.
- Consumer behavior prediction: Based on past purchase patterns and the digital footprint of the customer across channels, SKUs can be recommended, a tiered loyalty structure can be proposed across customer segments and up-selling and cross-selling can be done in an autonomous and self-learning way that enhances customer experience and reduces manual effort.
- Shelf space allocation: Improved visual merchandising can be done using agents, by taking in data around customer in-store behavior (where they spend greater amount of time), SKU sales velocity, the period of the year and other parameters. This can lead to a determination of the ideal number of facings of SKUs and placement across aisles. The entire process can be made autonomous using an agent, given the right training data and merchandisers allowing the agent to get initiated.
- Automated promotion and discount optimization: A tiered promotion and loyalty structure can be created using data from customer data platforms (CDPs), SKU-level details across stores and channels and other parameters.
- Automated replenishment: Based upon SKU availability, safety stock guidelines, the type of SKU (critical/regular) and other inventory parameters, replenishment schedule can be triggered by agents, from the generation of POs for the CPGs/manufacturers to order fulfilment.
- Packaging design and optimization: Packaging look and size, the material for packaging and packaging weights can be improved using data from social listening and customer sentiment analysis. Agents can also determine the packaging lifecycle workflow, including determining package ingredients and recyclability) in an autonomous fashion.
- Inventory optimization: Determining the optimal inventory quantity to be held at each supply chain node, from DCs to FCs to stores and including inventory for the omnichannel route, can be done using agents in a seamless manner. By consuming data across company sales, forecast, storage locations, SKU details like perishability and others, AI agents can perform a major part of inventory optimization, including allocating requisite amounts to each node.
Many more use cases can also be imagined for CPG organizations.
How to operationalize AI agents
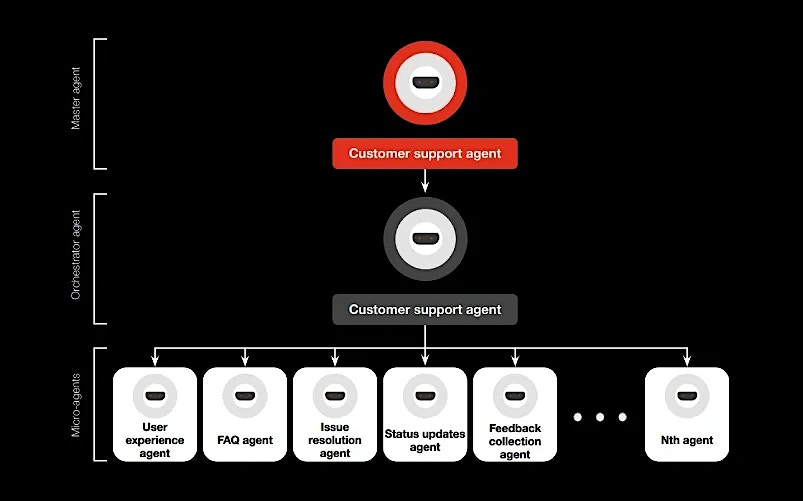
A simple, yet effective, way to go about designing agents for a CPG organization can be to consider a master agent with an orchestrator agent underneath it, followed by a set of micro-agents, each of which serves a specific purpose.
Real-world examples
Let's examine some CPG examples where firms are leveraging agents.
Unilever – Human resources - The firm employs agents to screen candidates by analyzing video interviews and responses, allowing human recruiters to focus on the most promising applicants.
Technology stack:
- AI models: NLP and facial recognition algorithms
- Frameworks: Multimodal candidate assessment platforms
- Tools: HireVue AI platform
Financial impact:
- Cost reduction: Saved over USD 1 MN annually in recruitment costs
- Efficiency gains: Reduced hiring time by 75%
Non-financial benefits:
- Enhanced diversity in hiring
- Improved candidate experience
Coca-Cola – Marketing – Using agents, the firm generates marketing content, analyzes consumer trends and personalizes advertising, leading to more effective campaigns.
Technology stack:
- AI models: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
- Frameworks: Multimodal data analysis for consumer insights
- Tools: Custom AI platforms
Financial impact:
- Efficiency gains: Reduced content creation time by 50%
- Revenue increase: Boosted campaign ROI by 20%
Non-financial benefits:
- Innovative marketing strategies
- Enhanced customer engagement
With adoption of Agentic AI getting more widespread, the number of live use cases employing agents will skyrocket soon enough.
Next steps
A well-crafted roadmap is essential to harness the power that AI agents bring to the table. Below is a simplistic representation:
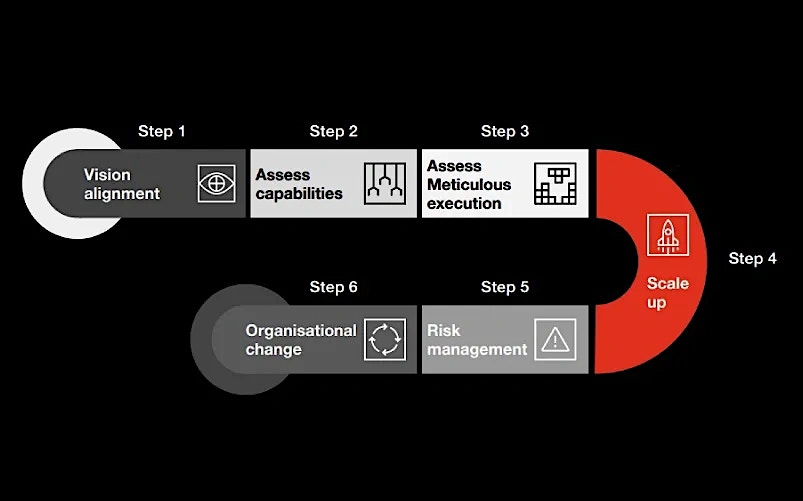
A few steps to keep in mind:
Vision alignment:
- Define clear objectives – What do you aim to achieve? For example, cost reduction, revenue growth, customer satisfaction or building a strategic ‘moat’ of differentiation.
- Align AI initiatives with business goals – To maximize impact.
- Secure executive sponsorship – Helps to secure resources and drive organization change, including any disruption within job roles that AI agents can potentially create.
- Start with high-impact, quick-win use cases – To have a clear path to ROI for the business.
Assess capabilities:
- Technology infrastructure – Is your IT environment ready for AI agents’ integration?
- Platform options – Build vs. Buy decisions
- Data readiness – Do you have access to quality, multimodal data?
- Skillsets – Do you have skillsets in-house? Experienced vendors, including niche digital consulting firms and the regular SIs, can help here.
The next frontier
“AI agents will become an integral part of our daily lives, helping us with everything from scheduling appointments to managing our finances. They will make our lives more convenient and efficient” – commented Andrew Ng, the co-founder of Google Brain. With such a seeming prowess, it’s only natural that businesses have sat up and started noticing. The question remains, can AI agents be made more pervasive across front-end and operational modules for CPG companies?
The answer to that might just draw the line between leaders and laggards within a thriving CPG industry.





